2025-11-07 20:28 Tags:
Definition
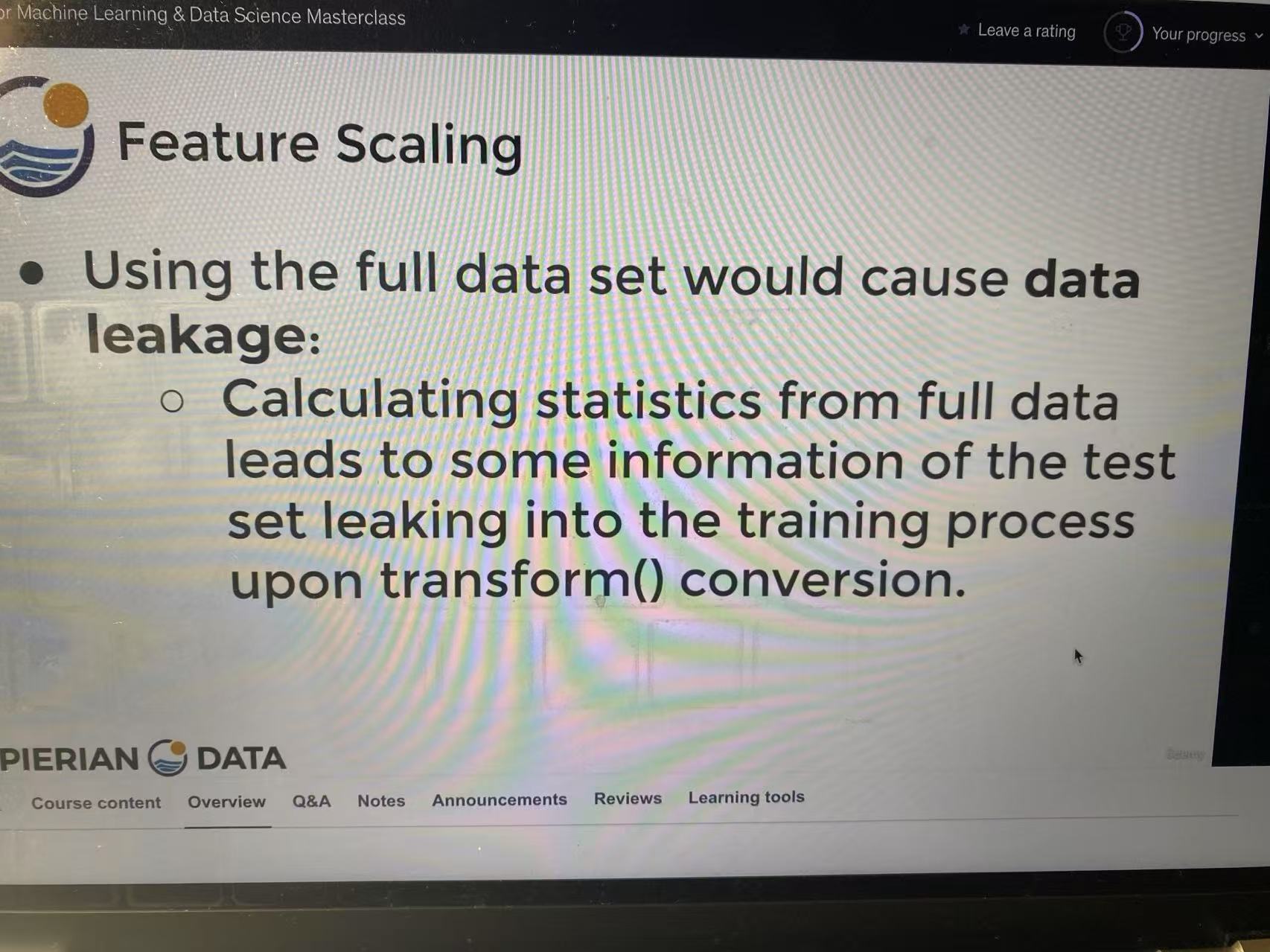
Feature scaling is the process of transforming numerical variables so that they share a similar range or distribution.
This prevents variables with large numeric ranges from dominating model training.
Why It Matters
Machine learning algorithms rely on distance or gradient-based optimization.
If features have very different scales (e.g., age = 0–100 vs. income = 0–100000),
the algorithm may:
-
Take uneven optimization steps
-
Converge slowly or not at all
-
Give undue weight to large-magnitude features
Feature scaling makes optimization faster and more stable. If you don’t know whether you need to do the feature scaling, then just do it, there is no ‘real’ drawback.
Common Methods
 most two ways:
most two ways:
- standardization Z score which is Normal Distribution
- normalization range 0-1
Algorithms That Need Scaling
| Needs Scaling | Doesn’t Need Scaling ❌ |
|---|---|
| Gradient-based models (Linear/Logistic Regression, Neural Nets) | Tree-based models (Random Forest, XGBoost) |
| KNN, K-Means, PCA, SVM | Naive Bayes |